ABIS uses Multi-Biometric Identification for Diverse Applications.
An Automated Biometric Identification System (ABIS) is a sophisticated technology that matches biometric features from an individual, such as fingerprints, facial recognition, or iris scans, against a database to verify identity. The process begins with the capture of biometric data, where a scanner or camera records the individual’s unique physical characteristics. This data is then converted into a digital format, creating a biometric template. When identification is needed, the system compares the live capture of biometric data against the stored templates in the database. If there’s a match, the system confirms the identity of the individual. ABIS is widely used for security purposes, immigration control, and law enforcement, providing a high level of accuracy in identifying individuals.
ABIS Main Components
Biometric Data Capture
Capture biometric data using hardware such as fingerprint scanners or facial recognition cameras to ensure accurate collection of biometric samples.
Enrollment Software
Manage the initial capture, quality assessment, and feature extraction of biometric data, ensuring high-quality templates are created for storage and comparison.
Biometric Database
Store biometric templates and associated metadata in a secure, scalable database designed to handle large volumes of data and efficient matching processes.
Matching Engine
Compare captured biometric samples against stored templates using advanced algorithms and machine learning techniques, ensuring fast and accurate identification.
System Middleware
Facilitate communication and integration between various components of the ABIS, including data capture devices, the biometric database, and external systems.
Administration Tools
Provide users with the ability to manage the ABIS, monitor its performance, and perform necessary maintenance tasks. Enable the enrollment, search, and verification of biometric data through interfaces.
Security and Privacy
Ensure the protection and confidentiality of biometric data throughout the system with robust security measures and privacy controls, including encryption, access controls, and regulations compliance.
Reporting and Analytics
Generate reports and analyze system performance, usage statistics, and biometric match results, aiding in decision-making and improving the biometric identification process.
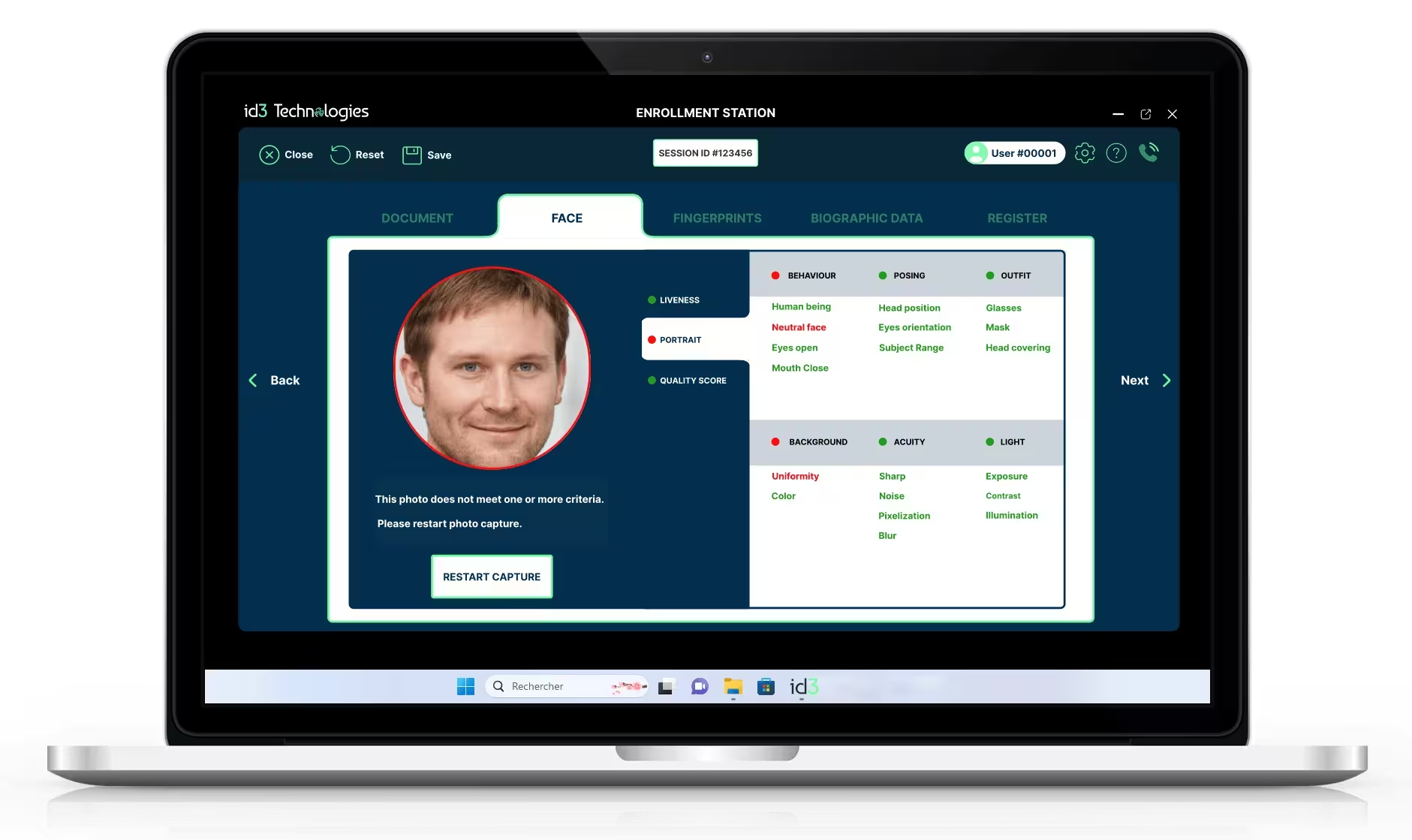
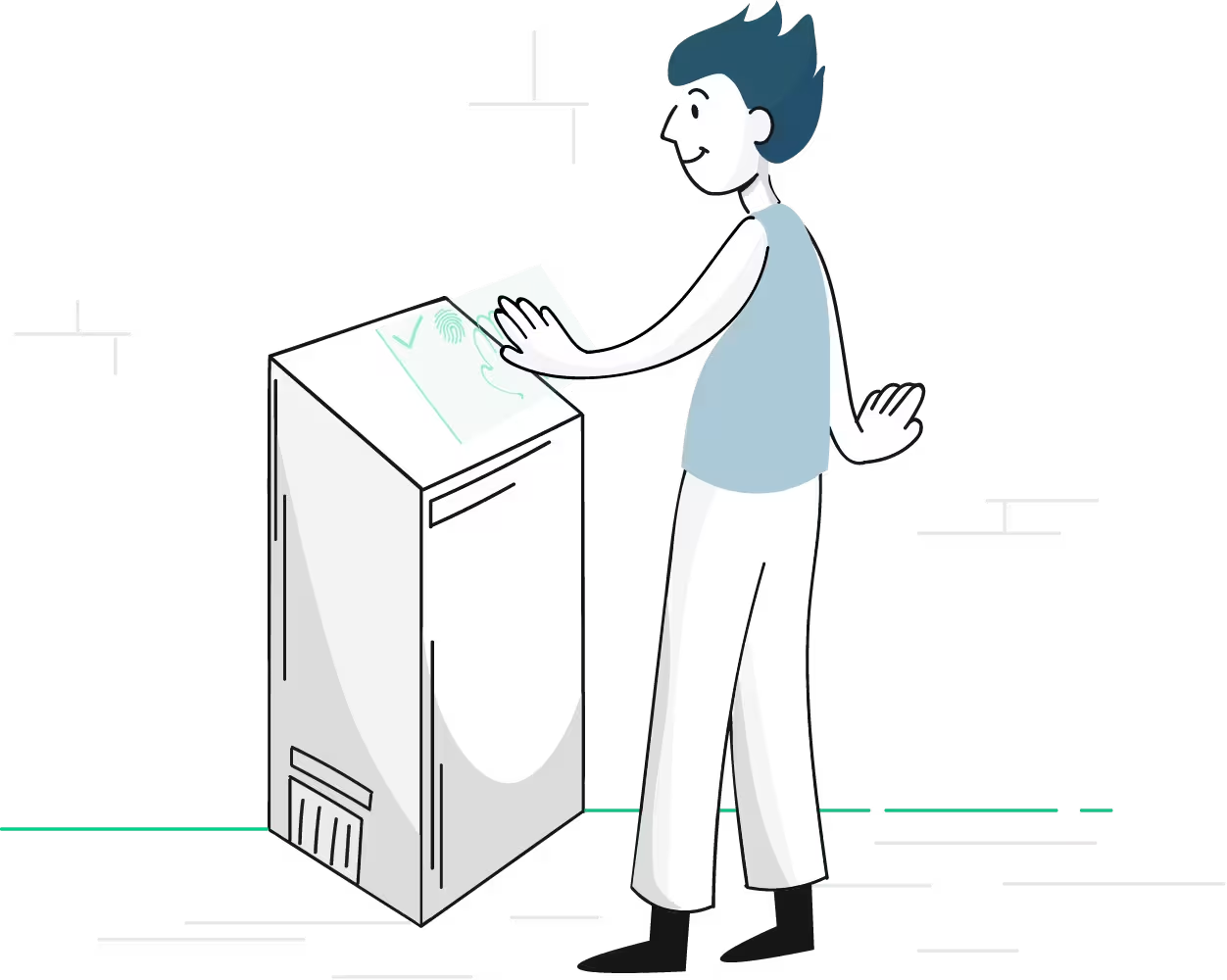
High biometric data quality.
Enrollment software.
Ensuring high-quality templates during enrollment is crucial for accurate and reliable automated biometric identification system. Our enrollment software captures high-quality biometric samples such as fingerprints, or facial images. It then assesses image quality to meet predefined standards, ensuring data reliability. Finally, it extracts unique features from the biometric data to create precise and reliable templates. This structured process maintains the highest standards of biometric data quality such as ICAO, leading to accurate and secure identification outcomes.
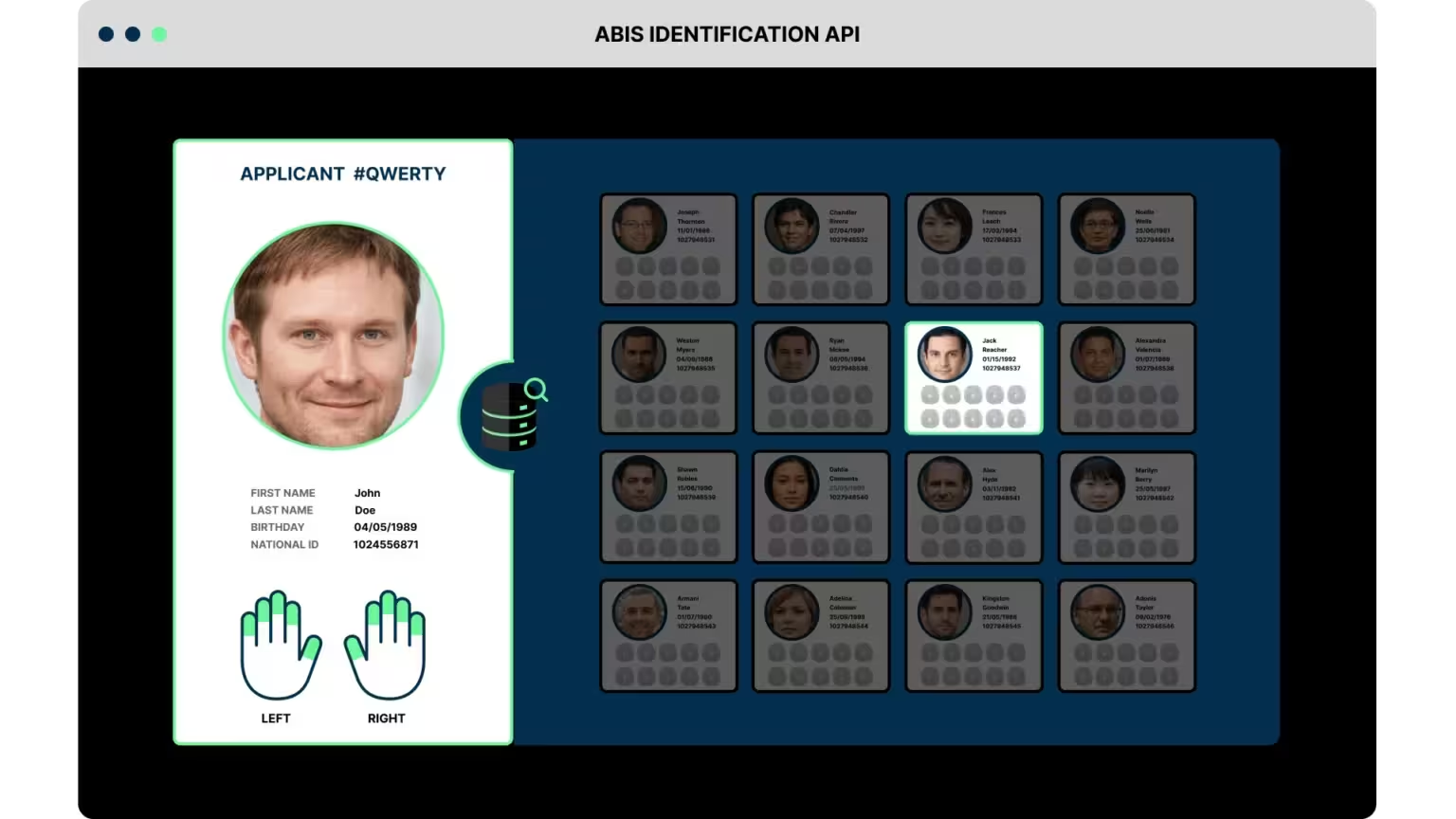
Large scale identification.
Deduplication process.
Once registered, the system compares the person’s biometric data with existing records to determine whether the identity is unique or not. Our ABIS match server performs a 1:N identification process against the reference database and returns match scores for each identity. The comparison thresholds (FMR/FNMR) can be configured according to customer needs. If no potential matches are found the applicant identity is saved as a new reference in the database.
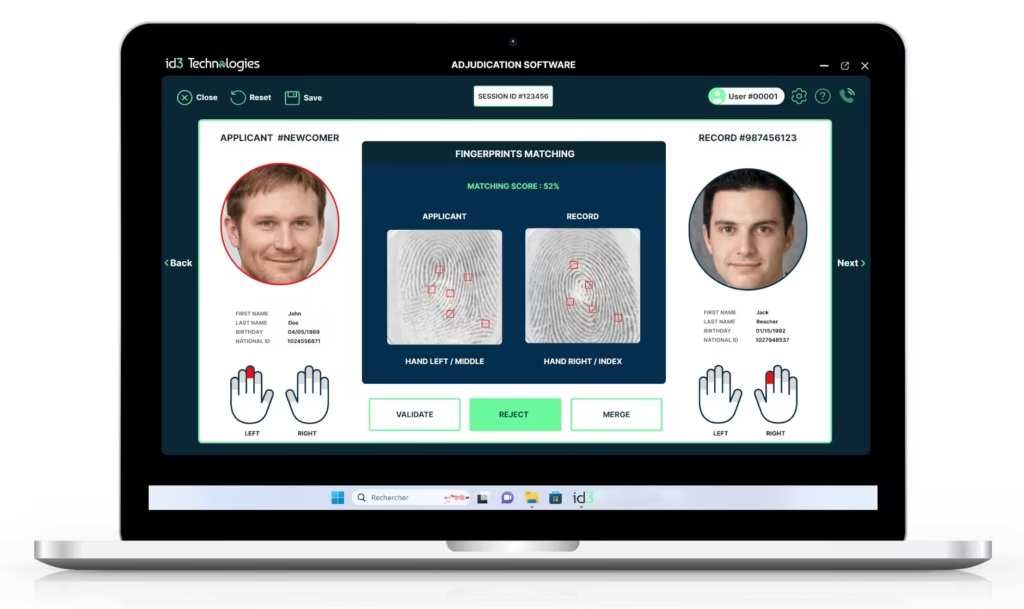
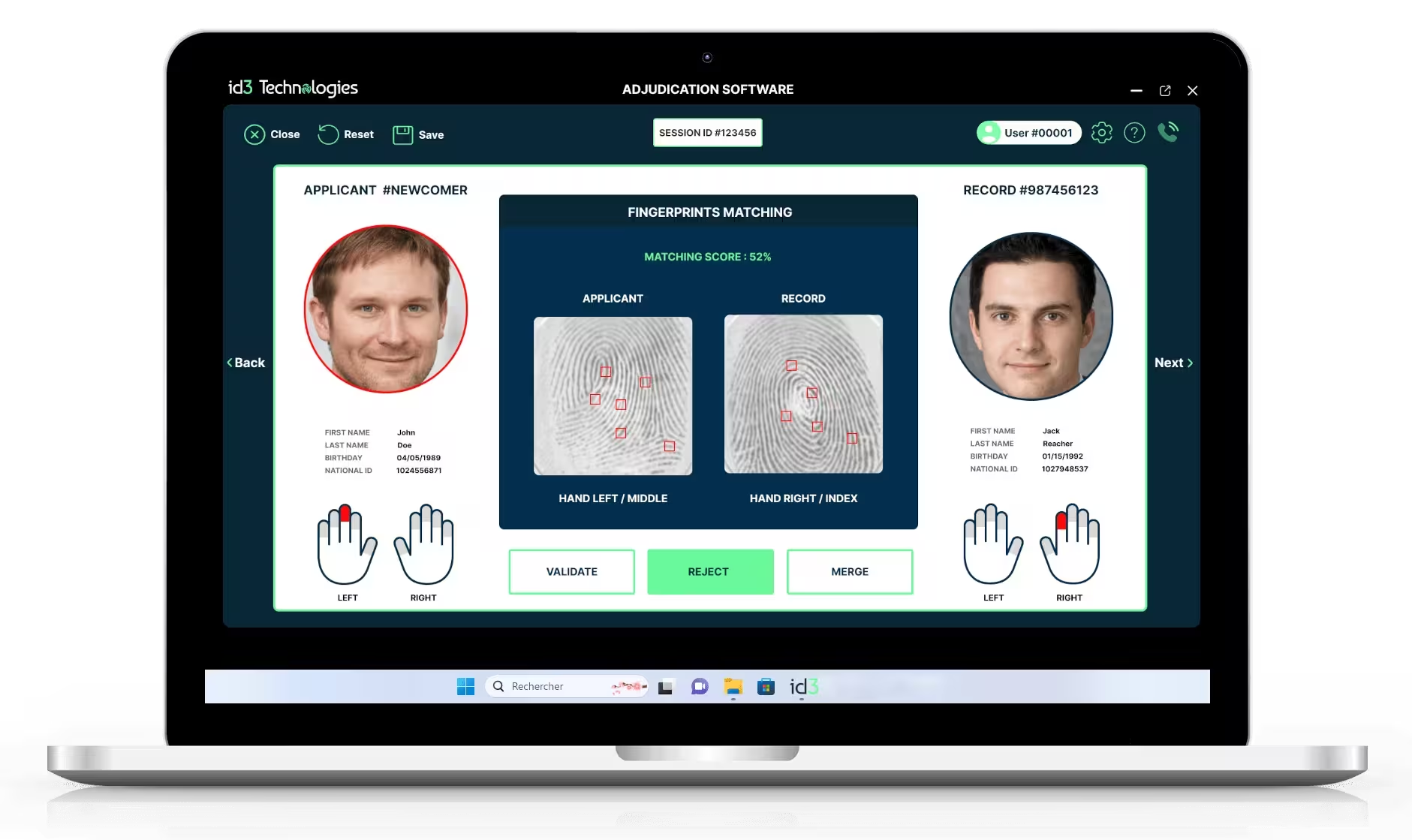
Matching decision helper.
Adjudication tool.
After the automated de-duplication steps, an adjudicator steps in. His role is critical. He reviews the results from the automated biometric identification system or other matching processes. Based on the evidence, he makes an overall decision: “match” (if the biometrics match an existing record) or “no match” (if they don’t). This manual decision ensures that the ABIS maintains accuracy and prevents false positives or negatives.
Identity Management System.
An Identity Management System (IMS) is a comprehensive framework that encompasses processes and technologies used to manage and secure user identities within an organization. An IMS ensures that users (employees, customers, suppliers) have appropriate access to specific applications, preventing internal vulnerabilities and distinguishing legitimate users from potential attackers.Here are the key components of an IMS.
User Registration and Provisioning
The process begins with user registration, where individuals provide their identity information such as name, email, and other relevant details. The IMS then validates this information and assigns a unique identifier to each user. User provisioning involves granting appropriate access rights and privileges based on roles, responsibilities, or organizational hierarchy.
Authentication
Authentication is the process of verifying the identity of users attempting to access the system. IMS employs various authentication methods such as passwords, biometrics (fingerprint, retina scan, etc.), tokens, or multi-factor authentication (MFA) for enhanced security. Upon successful authentication, users are granted access to authorized resources based on their assigned roles and permissions. Authorization determines what actions users are permitted to perform within the system. IMS uses access control policies configured by administrators to enforce authorization rules. These policies define who can access specific resources, what operations they can perform, and under what conditions
Single Sign-On (SSO)
SSO is a feature of IMS that allows users to access multiple applications or systems with a single set of credentials. Once authenticated to one application, users can seamlessly access other authorized applications without having to log in again. This enhances user experience and productivity while simplifying password management for users and reducing the risk of password-related security issues.
Identity Federation
Identity Federation enables trust relationships between different IMS instances or between an organization and external service providers. It allows users from one organization to access resources in another organization’s IMS seamlessly, without the need for separate authentication. This is particularly useful in collaborative environments, where organizations need to share resources securely across boundaries.
Lifecycle Management
IMS manages the entire lifecycle of user identities, from initial registration to eventual de-provisioning. It includes processes such as account creation, modification (e.g., role changes, updates to user attributes), suspension, reactivation, and termination. Proper lifecycle management ensures that user access remains aligned with business requirements and security policies throughout their association with the organization. IMS logs and monitors user activities within the system for auditing and compliance purposes. It maintains detailed records of authentication events, access requests, and administrative actions. These audit logs help organizations track user behavior, detect anomalies, and demonstrate compliance with regulatory requirements.
Integration with Directory Services
IMS often integrates with directory services such as LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) or Active Directory for centralized user management. This integration streamlines user provisioning, authentication, and authorization processes by leveraging existing user data stored in the directory.
Applications
Border Control
Streamline and secure border control processes by verifying travelers’ identities using ABIS with biometric data such as fingerprints or facial recognition.
Criminal Identification
Assist law enforcement by matching biometric data from crime scenes with existing databases to identify suspects and criminals accurately.
Healthcare
Ensure secure access to patient information and medical records in healthcare, protecting against identity theft and maintaining data integrity.
Financial Services
Enhance security in banking by using biometric authentication to prevent fraud and ensure only authorized users can access financial accounts and perform transactions.
Get started with our technologies.
Contact us to learn more about our biometric and security solutions and discover how it can transform your products and services. With id3 Technologies, step into a world where technology meets security, innovation, and reliability.